The
AMIGA project: Analysis
of the interstellar Medium of Isolated Galaxies
The core team of this group is located at the
Instituto
de Astrofísica de Andalucía. IAA (Spain):
Lourdes Verdes-Montenegro
(Staff, P.I.)
Daniel Espada
(PhD student)
Emilio J. García (System Manager)
Stéphane Leon (PostDoc)
Ute Lisenfeld (PostDoc)
José Sabater (Graduate student)
Simon Verley (PhD student)
and the main
co-workers are:
Jack
Sulentic (University of Alabama
- USA), Walter Huchtmeier (Max Planck Institute
of Bonn - Germany), Steven Odewahn (Mc
Donald Observatory - USA), Min S. Yun (FCRAO - USA), Soledad
del Rio INAOE (México), Francoise
Combes (Paris
Observatory - France).
The project
A key problem in astronomy involves the role of the
environment in the formation and evolution of galaxies.
In order to answer this question it is necessary to characterize
a reference sample with minimum influence from the environment,
so that its evolution is completely determined by nature.
The aim of this project is to provide such reference,
quantifying the ISM properties of a well defined and
statistically significant sample of 760 isolated galaxies.
Based on optical, Halpha and infrared luminosities,
radio continuum emission, molecular and atomic gas
content, compiled from the bibliography or observed
by ourselves, together with POSS-I and POSS-II digitized
images, we will perform an statistical study of the
ISM properties as function of isolation, and in
connection with star formation, morphology and luminosities,
as well as nuclear activity frequency.
This sample will be different from previous studies
by three essential characteristics:
a) strict definition
of isolation,
b)
statistical significance, and
c) complete multi wavelength
information concerning the ISM.
It will serve to evaluate
the properties of interacting galaxies, and this will
be of special interest to analyze the large amount
of data that will be generated during the next decade
for high z galaxies, with the new instruments to
come.
We can summarize
the keys of our project in:
- A definition of “isolated galaxy”
is needed before one can properly assess the
history and properties of peculiar
ones.
- We are constructing
the first complete unbiased control sample of
the most isolated galaxies of the northern sky
(Verdes-Montenegro
et al 2001, 2002, 2003, Lisenfeld et al 2002ab) to serve
as a template in the study of star formation
and galaxy evolution in denser environments.
- Our goal is
to compare and quantify the properties of different
phases of the interstellar medium in this sample,
as well as the level of star formation, both
relevant parameters in the internal evolution of galaxies
and strongly conditioned by the environment.
- To achieve
this goal we are building a multiwavelength database
for this sample to compare and quantify the
properties of different phases of the ISM. Our source
list is based on the Catalog of Isolated Galaxies
(CIG; 1051 galaxies) and our sample contains ~800
galaxies.
The chosen wavelengths are:
- The optical luminosity as a tracer of the visible light,
stellar content and, in a rough way, the mass.
- The far-infrared emission where most of the flux from newly
formed stars is re-radiated.
- Atomic gas, as a fundamental ingredient of the ISM and a
very sensible tracer of interaction.
- Molecular gas, as the raw material for star formation
- Halpha emission, a good tracer of recent star formation in
places where extinction is not high.
- Radio-continuum emission as a useful tracer that is not affected
by extinction for the current SFR and for the nuclear activity.
- NIR luminosity: we are currently starting a NIR survey of
the sample, as a tracer of the bulk of the old stellar population.
Further information cocerning the project can be found in AMIGA web page.
The Halpha survey
This survey is part of the PhD work of Simon Verley. The CO and Halpha
study will concentrate on a smaller redshift-limited subsample, much preferable
from a flux-limited sample which unavoidably leads to biases, by restricting
the galaxies to recession velocities in the 1500 - 5000 km/s range. This gives
a subsample composed of 205 galaxies, large enough to evaluate multiwavelength
properties as a function of the
isolation degree.
The aims of our Halfa study are:
- To obtain a template for the global Halpha emission strength.
This will allow us to revise reported SF enhancements in strongly interacting
systems and unexpected SF inhibition in compact groups of galaxies (e.g.
Kennicutt et al. 1987, 1994, Hummel et al 1990, Gavazzi et al 1991,
1998, 2002, Young et al 1996, Jansen et al 2000, Boselli et al 2002, Iglesias-Páramo
et al 1999, 2002ab) all of them depending upon small or unhomogeneus control
samples.
- To investigate the dependence for isolated galaxies of Halpha derived
SF rates with HI, H2 and/or HI+H2, whose connection is not well defined yet
for other samples (Kennicutt 1988, 1989, 1998).
- To quantify Halpha morphologies: We will identify, and statistically
quantify, the morphologies of the Halpha light following our previous studies
of interacting pairs(e.g. Combes et al. 1994) that revealed at least 3-4 fundamentally
different morphologies in H$\alpha$ light (discrete emission: nuclear dominated
and/or disk dominated, as well as diffuse emission). With this purpose we
are producing HII regions catalogs from the images.
Status of the survey
Among the 205 galaxies composing the subsample, only 17 have data published
in the bibliography. We had two runs at the 2.2m CAHA telescope with CAFOS
(Jan. & Aug. 2003) but due to bad weather only 21 CIG galaxies
could be observed.
Some sample images are shown in Fig. 1.
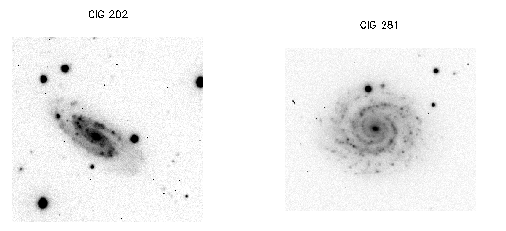
Figure 1. Halpha+continuum images obtained for CIG 202 and CIG 281 during
the January 2003 run, each corresponding to a 10 minutes exposure.
During various campains on 1-meter class telescopes we observed the 100
brighter galaxies.
Twelve more new moon days are currently scheduled at the CAHA 2.2m telescope
during the following semester.
We have started the extraction of HII regions from these data and an example
is shown in Fig. 2, 3 & 4.

Figure 2. R-continuum image obtained for CIG 0096.
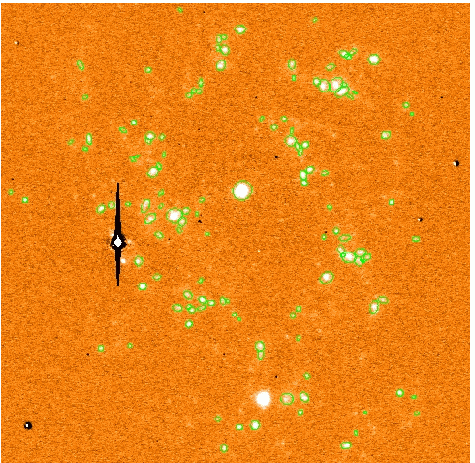
Figure 3. Halpha, continuum substracted image obtained for CIG 0096;
the green contours mark the HII regions extracted using SExtractor.
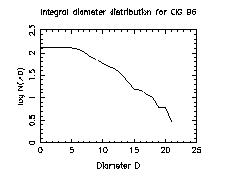
Figure 4. Integral diameter distribution for CIG 0096: we found that
the caracteristic diameter of the HII regions is 63 pc.



